Overview
Teaching: 0 min Exercises: 30 minQuestions
Objectives
Deploy a Django web framework on AWS Elastic Beanstalk
Learn how to use a Python IDE to build your web app
Prerequisites
- Miniconda or working version of Python (We are going to use Python 3.6 for most the work here)
- Pycharm
- Pycharm AWS Elastic Beanstalk plugin
- The Django project is available here: http://github.com/cloudmaven/cloud101demo
Deploying an Elastic Beanstalk App
Start PyCharm.
Create a python environment for your app. You can use the “terminal” tab at the bottom of your PyCharm app or use the regular terminal. Here I am using conda to create my environment:
conda create -n env_name python
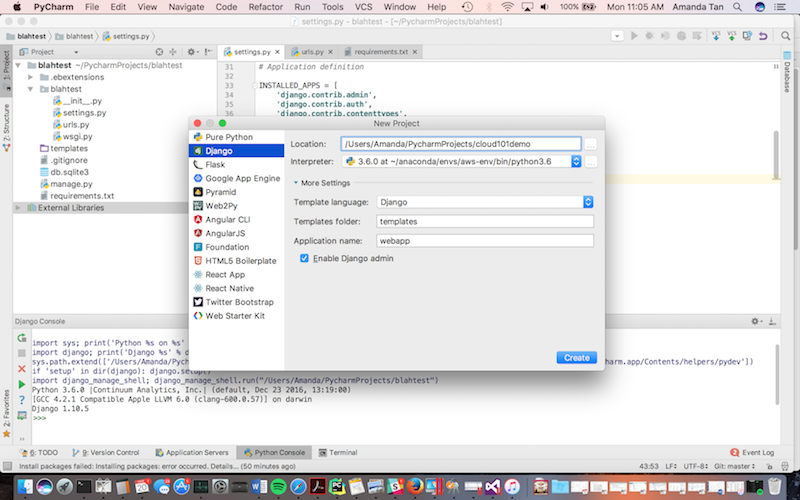
You are now ready to create your new project. From the File menu, select New Project then Django. Fill in the location where you want to save your project (Here I am saving it to /Users/Amanda/PycharmProjects/cloud101demo). You can call your project whatever you want. Then choose your interpreter. Click the little “…” button on the right of the Interpreter text box, select “Add local” then find the virtual environment that you created earlier. If you created your environment using conda, it should be in your home directory under anaconda. For example, my virtual environment will be stored in ~/anaconda/envs/aws-env/. You will want to add the Python interpreter created in that virtual environment. Here, I am using Python 3.6.0.
Under “More Settings”, give your application a name. Here I’m calling mine “webapp”.
You should now have a project with a folder structure that looks something like this:
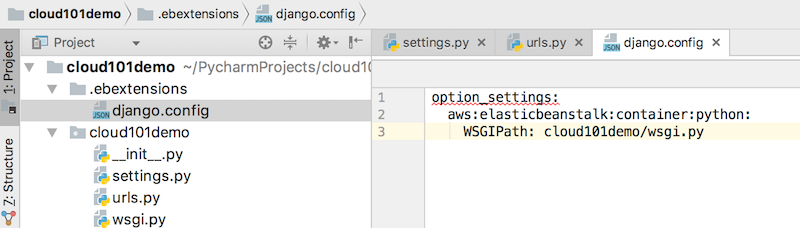
Create a folder named .ebextensions in the root of the project tree. This is the where AWS Beanstalk configuration files reside. Create a file named django.config inside the .ebextensions folder. Paste the following (remember to substitute beanstalkdemo for your project name):
option_settings:
aws:elasticbeanstalk:container:python:
WSGIPath: cloud101demo/wsgi.py
For Beanstalk, we are going to install two libraries - boto and django-storages. In the terminal in Pycharm, we will do
pip install boto django-storages
Next, you need a requirements file to tell Beanstalk which dependencies to install when you deploy your Django app. Again, in the terminal, do
pip freeze > requirements.txt
The contents of your file should look something like this:
appdirs==1.4.3
boto==2.46.1
Django==1.10
django-storages==1.5.2
packaging==16.8
pyparsing==2.2.0
six==1.10.0
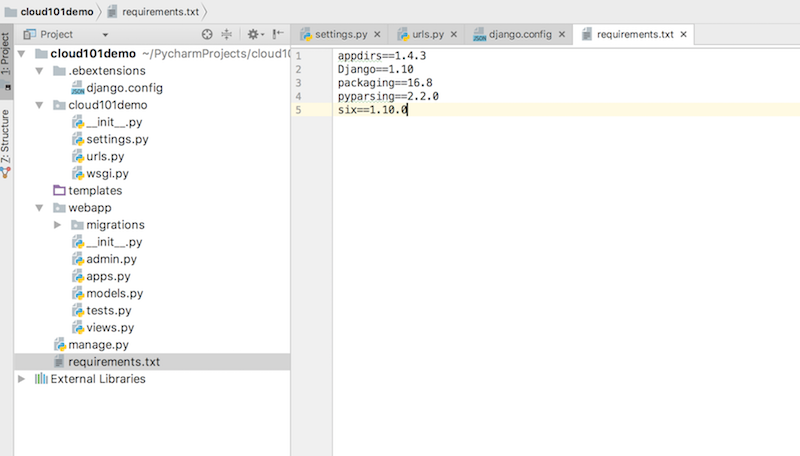
You should now have a directory structure that looks like this:
We will now build a couple of template files, the API scripts and the Leaflet map.
** Template Files (index.html and layout.html) **
Right click on Templates > New > Directory > app (this creates a folder named ‘app’)
Right click on Templates (app) > New > HTML File > layout.html The code is here: https://github.com/cloudmaven/cloud101demo_beanstalk/blob/master/templates/app/layout.html
Right click on Templates (app) > New > HTML File > layout.html The code is here: https://github.com/cloudmaven/cloud101demo_beanstalk/blob/master/templates/app/index.html
A couple of points to note here is that layout.html will be your default template. You can use this snippet at the top of every new html page. The layout html file also includes all the references to bootstrap, js and jsquery:
** settings.py **
Next, we are going to mess around with the settings. This is found in the settings.py file. You want to check that you have the name of your app included in your INSTALLED_APPS, e.g.:
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'app',
]
At the end of file, stick in the configuration to connect to your s3 bucket we created earlier that hosts all the geojson file e.g.:
BUCKET_NAME = 'cloud101demo'
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID = 'from your credentials'
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY = 'from your credentials'
Ok - let’s break for lunch because I’m hungry.
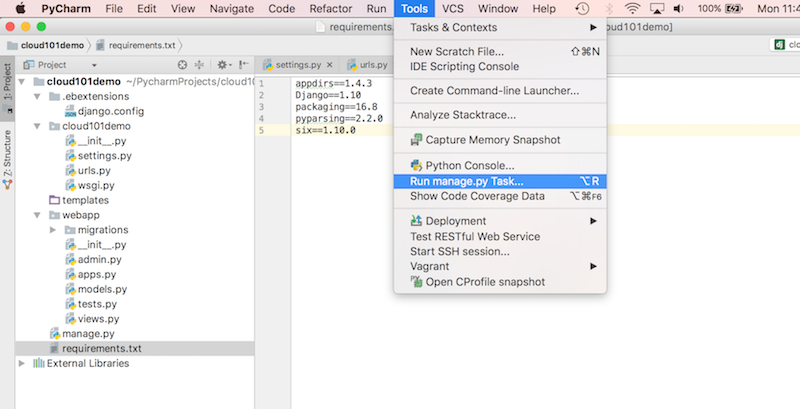
We can check the deployment of a generic Django website on your local machine. In the Tools dropdown menu, select Run manage.py Task
This will open up the manage.py console. Type migrate webapp then runserver:
You will see a sample Django application being deployed on http://127.0.0.1:8000/
Key Points